Module 10 patterns of inheritance
- 1. Genetics the study of heredity
- 2. Gregor Mendel “Father of Genetics” Heredity -the transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring through their genes Gregor Mendel -used garden peas to study heredity
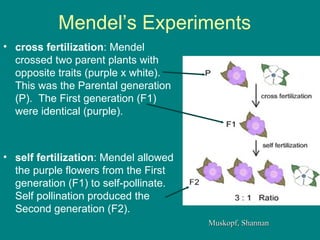
- 3. Mendel’s Experiments cross fertilization : Mendel crossed two parent plants with opposite traits (purple x white). This was the Parental generation (P). The First generation (F1) were identical (purple). self fertilization : Mendel allowed the purple flowers from the First generation (F1) to self-pollinate. Self pollination produced the Second generation (F2). Muskopf, Shannan
- 4. Mendel’s Conclusions The F1 generation all showed the purple trait (called the dominant trait) In the F2 generation the (white) trait reappears in ¼ of the flowers (called the recessive trait) Each flower has two alleles that determine the appearance The alleles are represented by letters (uppercase letter represents the dominant allele; lowercase letter represents the recessive allele) P is dominant and represents purple p is recessive and represents white The Dominant Is Expressed No Matter What Need 2 Copies Of The Recessive Allele In Order To Be Expressed PP = purple flower Pp = purple flower pp = white flower
- 5. Alleles homozygous: organisms that have 2 identical alleles for a trait (could be two capital or two lowercase letters) PP pp heterozygous: organisms that have 2 different alleles for a trait ex: Pp (the dominant allele P is expressed so this flower would be purple)
- 6. Genotype: letters used for the alleles ex: PP, Pp, pp Phenotype: what an organisms looks like ex: purple, white
- 7. Punnett square A Punnett square is used to show the possible allele combinations in the offspring of 2 parents. Monohybrid cross = cross involving only 1 trait The four boxes represent the four possible offspring
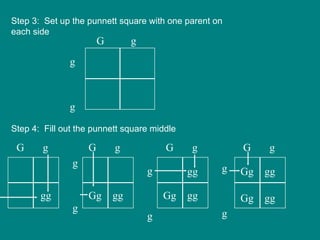
- 8. A plant heterozygous with green peas (Gg) is crossed with a plant that has yellow peas (g). Step 1: Choose a letter for the alleles (green is dominant; yellow is recessive) G : green pea g: yellow pea Step 2: Write the genotypes of the parents heterozygous plant with green peas : Gg plant with yellow peas: gg parents: Gg x gg Example of a Monohybrid Cross
- 9. Step 3: Set up the punnett square with one parent on each side Step 4: Fill out the punnett square middle G g g g gg gg gg gg Gg G g G g G g g g g g g g Gg Gg gg gg Gg G g g g
- 10. Step 5: Look at the four boxes from Step 5 and determine the genotypes of the four offspring Genotypic ratio: 2 Gg: 2 gg Step 6: Look at the genotypes in Step 6 and determine the phenotypes; Green (G) is dominant over yellow (g), plants that have G in their offspring have green peas Phenotypic ratio: 2 green: 2 yellow
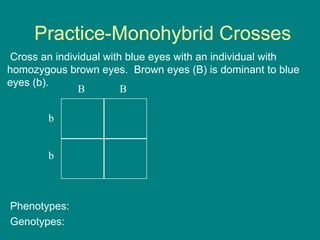
- 11. Practice-Monohybrid Crosses Cross an individual with blue eyes with an individual with homozygous brown eyes. Brown eyes (B) is dominant to blue eyes (b). Phenotypes: Genotypes: B B b b
- 12. Cross an individual with blue eyes with an individual with homozygous brown eyes. Brown eyes (B) is dominant to blue eyes (b). Phenotypes: All Brown Eyes Genotypes: All Bb B B b Bb Bb b Bb Bb
- 13. Practice-Monohybrid Crosses A child is diagnosed with a recessive genetic disease. Neither parent has the disease. What are the genotypes of the parents? Phenotypes: Genotypes: N ? ? nn N
- 14. A child is diagnosed with a recessive genetic disease. Neither parent has the disease. What are the genotypes of the parents? Genotypes of the parents are Nn N n n Nn nn N NN nn
- 15. Incomplete Dominance = Blending In snapdragons, there is not a dominant allele. The flower color can be red, pink, or white. A heterozygous flower (Rr) will a blending of red and white (pink). Muskopf, Shannan. Online Images. The Biology Corner . 20 April 2007. http://www.biologycorner.com/bio1/celldivision-chromosomes.html
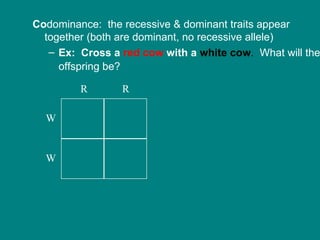
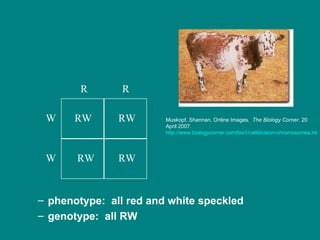
- 16. Co dominance: the recessive & dominant traits appear together (both are dominant, no recessive allele) Ex: Cross a red cow with a white cow . What will the offspring be? R R W W
- 17. phenotype: all red and white speckled genotype: all RW W RW RW W RW RW R R Muskopf, Shannan. Online Images. The Biology Corner . 20 April 2007. http://www.biologycorner.com/bio1/celldivision-chromosomes.html
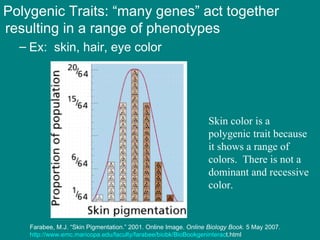
- 18. Polygenic Traits: “many genes” act together resulting in a range of phenotypes Ex: skin, hair, eye color Skin color is a polygenic trait because it shows a range of colors. There is not a dominant and recessive color. Farabee, M.J. “Skin Pigmentation.” 2001. Online Image. Online Biology Book. 5 May 2007. http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/biobk/BioBookgeninterac t.html
- 19. Multiple Alleles : genes that have more than two alleles There are four blood types (phenotypes): A, B, AB, and O Blood type is controlled by three alleles: A, B, and O Each individual only inherits two alleles (one from each parent). A and B are codominant O is recessive, two O alleles result in type O Blood Blood Types Possible Genotypes Dominant A AA or AO Dominant B BB or BO Codominant AB AB Recessive O OO
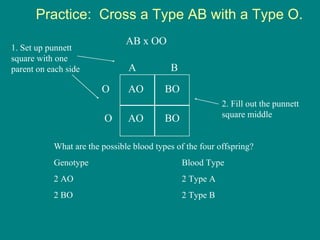
- 20. Practice: Cross a Type AB with a Type O. AB x OO A B O AO BO O AO BO 1. Set up punnett square with one parent on each side 2. Fill out the punnett square middle What are the possible blood types of the four offspring? Genotype Blood Type 2 AO 2 Type A 2 BO 2 Type B
- 21. A woman heterozygous for Type A blood marries and a man with Type AB blood. Show the cross and the possible offspring. 1. Write the genotypes of the parents: woman heterozygous for Type A: AO man with Type AB: AB 2. Set up punnett square with one parent on each side and fill in the middle. Practice A O A AA AO B AB BO Blood types of possible offspring: AA: Type A blood AO: Type A blood AB: Type AB blood BO: Type B blood
- 22. If a Type O individual marries a Type B individual can they have offspring with Type O blood? What type of blood can the offspring have? Practice B ? O O Blood types of possible offspring: AA: Type A blood AO: Type A blood AB: Type AB blood BO: Type B blood
- 23. If a Type O individual marries a Type B individual can they have offspring with Type O blood? What type of blood can the offspring have? B O O BO OO O BO OO Yes, they can have a child with type O or type B blood.
- 24. If 2 individuals with Type AB blood marry, what percentage of their offspring will have Type AB blood? Practice A B A B
- 25. 50% of their offspring could be Type AB A B A AA AB B AB BB If 2 individuals with Type AB blood marry, what percentage of their offspring will have Type AB blood?
- 26. Review of Terms Allele A form of a gene Homozygous Both Alleles are the Same Heterozygous Alleles are Different Homozygous Dominant AA Homozygous Recessive aa Heterozygous Aa Genotypic Ratio 2 PP : 2 pp Phenotypic Ratio 2 Purple : 2 White